The method was tested first using synthetic point data. This consisted
of clusters of 3-D points on a moving sphere projected onto the image
plane. Eight clusters were used and the surface
was translated along all three axes while rotating about the
x and y axes. The focal length was 1.0 and all
points were visible over all frames using a 53 degree field of view. Each
cluster occupied approximately 6.5 degree corresponding to 11% of the
image plane. Affine motion parameters were obtained for each cluster
using a least-squares fit amongst the corresponding points and
Gaussian noise was added to each parameter. Figure
3 shows the variation of the 6 noisy measurements
over time for one of the clusters where the noise standard deviation
for each parameter was set to approximately 10% of its maximum
(absolute) value. For these measurements, the evolution of the true
and estimated 3-D parameters over 200 frames is shown in Fig.\
4, where the structure is shown as the slant
![]() and tilt
and tilt ![]() of the surface normal and the depth D. Note
that the motion and inverse focal lengths converge rapidly, whilst the
structure converges within 100 frames (the translations and depths
converge to within a common scale factor). Convergence is rapid for
all the states when uncorrupted measurements are used.
of the surface normal and the depth D. Note
that the motion and inverse focal lengths converge rapidly, whilst the
structure converges within 100 frames (the translations and depths
converge to within a common scale factor). Convergence is rapid for
all the states when uncorrupted measurements are used.
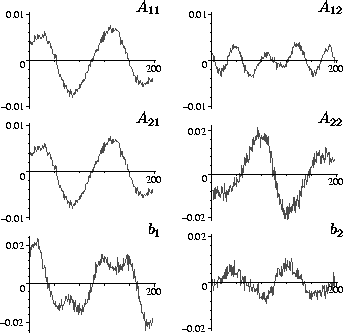
Figure 3: Noisy affine flow parameters for a cluster used in the point data experiment.
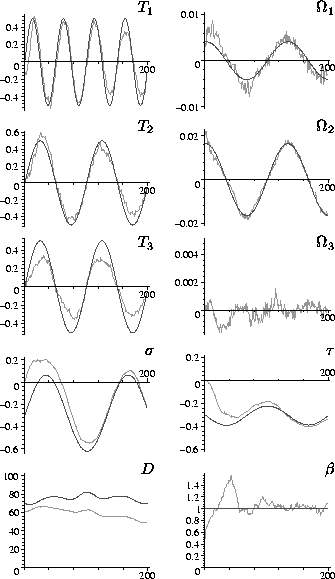
Figure 4: Motion, inverse focal length and structure estimates compared
with the known groundtruth (dark lines) for the point data
experiment.